Modulation and manipulation
Modulation is the process of changing certain parameters of a higher—frequencycarrier (modulated) signal that acts as an information carrier using a modulating signal that lays down information.
Modulation can be analog and digital. Analog refers to the types of modulation in which the frequency, amplitude or phase of a sinusoidal signal physically changes. Digitally, code symbols are converted into a sequence of signals.
Types of analog modulation:
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a type of modulation in which the variable parameter is the amplitude.
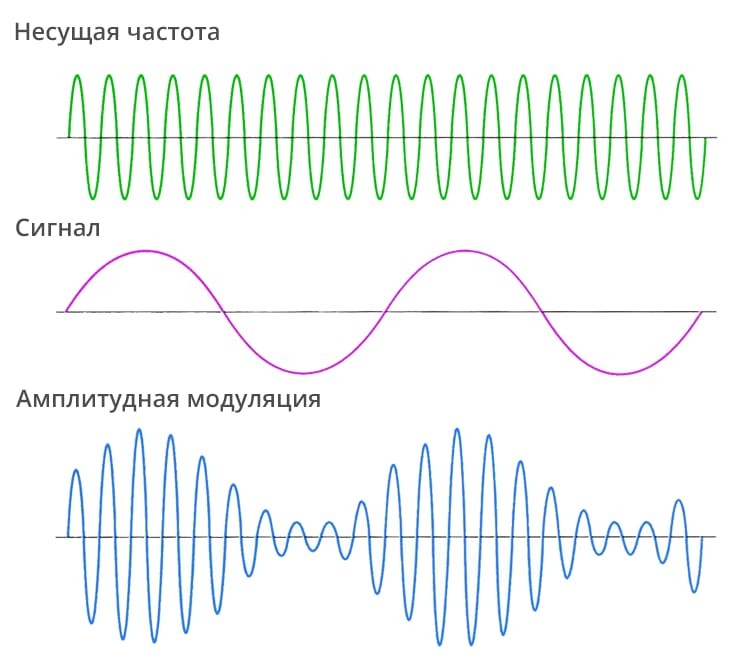
The first experiments on transmission with its help were carried out back in 1906 by the Canadian and American engineer R. Fessenden. In his experiments, an electric machine generator generated a signal with a frequency of 50 kHz, then a carbon microphone was switched on in the circuit, changing the resistance of the circuit, after which an antenna was installed. Being the very first type of modulation widely used in practice, it has become very widespread.

Reginald Orbie Fessenden
There is also a type of amplitude modulation with one side signal (SSB), where one of the two mirror side bands is «cut off», and then the receiver restores the carrier without loss of information. Depending on which band was excluded, the SSB may be in the upper side band or the lower one.
Frequency modulation (FM) is a type of modulation in which the variable parameter is the frequency, and the amplitude remains unchanged.
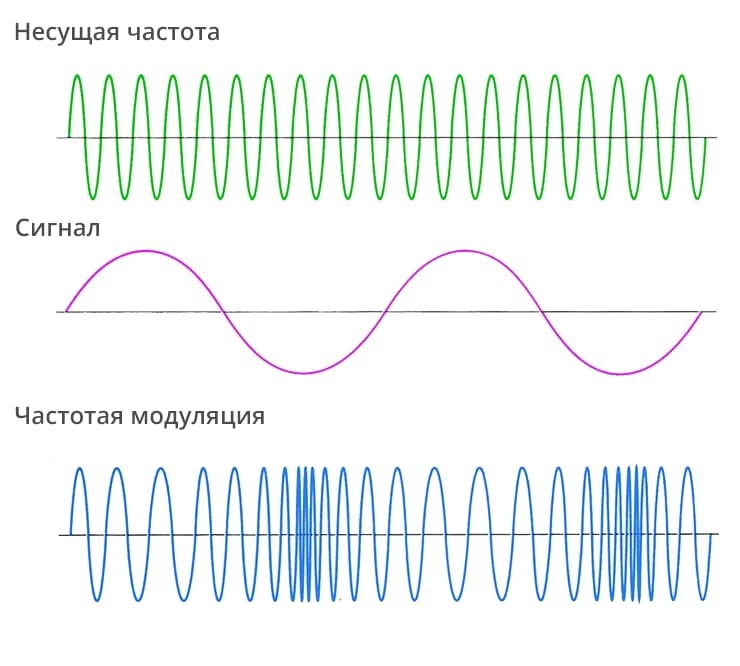
Cornelius D. Ehret invented frequency modulation in 1902, but for more than 30 years the invention has not found practical application. In 1933, Edwin Armstrong proposed the use of FM for radio broadcasting, which would reduce the total amount of interference. And in 1935, the first demonstration of radio communication with its use took place. It is more difficult to implement, compared to the amplitude one, but thanks to the advantages it has become extremely popular and is now considered one of the main ones.

Edwin Howard Armstrong
Linear frequency modulation is a subspecies of frequency modulation in which the frequency of the signal varies according to a linear law.
Phase modulation (PM) is a type of modulation in which the frequency and amplitude remain unchanged, the transmission of information occurs due to a change in the phase of the carrier oscillation in direct proportion to the information signal, also information can be transmitted not in the phase itself, but in the phase difference of neighboring signals in sequence, this is a relative phase manipulation (OFM). In terms of characteristics, it is close to frequency modulation. In fact, this is where the topic of digital modulation begins.
Digital modulation (manipulation) is the process of converting encoded characters into a sequence of signals. The waveform in it is often «square»
Types of manipulation:
Digital phase modulation (FSK) is a type of phase modulation in which the phase changes according to a sequence of zeros and ones.
Amplitude manipulation (AMn) -
Frequency Manipulation (FMn) -

